2.10 About Germany
Location
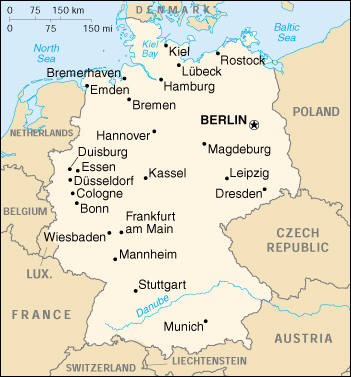
 The Federal Republic of Germany is the largest of the German-speaking countries. It is located in Central Europe, and has nine neighbours - Denmark to the North, Netherlands, Belgium, Luxemburg and France to the West, Switzerland and Austria to the South, and the Czech Republic and Poland to the East. This central location has been more pronounced since 3rd October 1990, when Germany was reunited. Due to its central position Germany functions within the EU and NATO as a bridge to the Central and Eastern European states and is an important location for European and global relations. The Federal Republic of Germany is the largest of the German-speaking countries. It is located in Central Europe, and has nine neighbours - Denmark to the North, Netherlands, Belgium, Luxemburg and France to the West, Switzerland and Austria to the South, and the Czech Republic and Poland to the East. This central location has been more pronounced since 3rd October 1990, when Germany was reunited. Due to its central position Germany functions within the EU and NATO as a bridge to the Central and Eastern European states and is an important location for European and global relations.
Reunified Germany now is now the sixth largest country in Europe with an area of 137,826 square miles (356,970 sq. km.). Western Germany comprises just over two-thirds of this - 96,095 square miles compared with 41,731 square miles in the former Eastern Germany. Germany extends 876 kilometres from its northern border with Denmark to the Alps in the south, and (at its widest) 650 kilometres from the Belgian border in the west to the Polish frontier in the east. The total length of the country's borders is 3,758 kilometres.
Population
 Germany has a population of approximately 82.163 million, the largest in Europe after the Russian Federation, followed by the United Kingdom (58.9 million), France (58.5 million) and Italy (57.5 million). About one fifth of this population live in the former GDR. Germany has a population of approximately 82.163 million, the largest in Europe after the Russian Federation, followed by the United Kingdom (58.9 million), France (58.5 million) and Italy (57.5 million). About one fifth of this population live in the former GDR.
The Federal Republic of Germany is a densely populated country, with a population density of 230 persons per square kilometre. More than half the German people live in towns with a population of between 2,000 and 100,000. There are 86 larger towns and cities with more than 100 000 inhabitants spread throughout the country. The five largest cities are Berlin, the official capital with a population of 3,458,800, Hamburg (1,708,500), Munich (1,232,800), Cologne (964,400), and Frankfurt (646,400).
There are 7,363,600 foreigners currently living in Germany, which is equal to 8.9% of the population. Just over two million of these come from Turkey, with other sizable immigrant communities coming from the former Yugoslavia, Italy, Greece, Africa and Eastern Europe.
Climate
 The Federal Republic's climate is determined by its location in a zone of temperate climatic conditions with frequent weather changes. There is precipitation all the year round. In the winter the average temperature is between 1.5°C in the lowland areas and -6°C in the mountains. In the warmest month of the year, July, temperatures are between 18°C in low-lying regions and 20°C in the sheltered valleys of the south. Progressing from the northwest to the east and southeast, the maritime climate gradually changes into a more continental climate. The Federal Republic's climate is determined by its location in a zone of temperate climatic conditions with frequent weather changes. There is precipitation all the year round. In the winter the average temperature is between 1.5°C in the lowland areas and -6°C in the mountains. In the warmest month of the year, July, temperatures are between 18°C in low-lying regions and 20°C in the sheltered valleys of the south. Progressing from the northwest to the east and southeast, the maritime climate gradually changes into a more continental climate.
Geography
 The whole of northern Germany, through which run the Weser, the Elbe, and smaller rivers, is set in the North European Plain. The Rhine Basin encompasses some of the most beautiful landscape and best wine-growing regions in Europe. Towards the east, this consists of morainic hills
containing fertile loess soil. More than a quarter of the whole of Germany is covered with forest. Among the major ranges of the mid-German highlands are the Teutoburger Wald, the Harz Mountains, the Sauerland, Westerwald, and Taunusgebirge. In the west are the Ruhr coalfields, while in the east there are large lignite deposits. Southward the ground gradually rises to the Black Forest (der Schwarzwald), and the Swabian Jura, with dense pine forests and moorland, and potash, salt, and other minerals. In Bavaria, further south, the land becomes rugged. Here are patches of mountain pasture and lakes; to the east is the deep Danube valley. The whole of northern Germany, through which run the Weser, the Elbe, and smaller rivers, is set in the North European Plain. The Rhine Basin encompasses some of the most beautiful landscape and best wine-growing regions in Europe. Towards the east, this consists of morainic hills
containing fertile loess soil. More than a quarter of the whole of Germany is covered with forest. Among the major ranges of the mid-German highlands are the Teutoburger Wald, the Harz Mountains, the Sauerland, Westerwald, and Taunusgebirge. In the west are the Ruhr coalfields, while in the east there are large lignite deposits. Southward the ground gradually rises to the Black Forest (der Schwarzwald), and the Swabian Jura, with dense pine forests and moorland, and potash, salt, and other minerals. In Bavaria, further south, the land becomes rugged. Here are patches of mountain pasture and lakes; to the east is the deep Danube valley.
Economy
 Germany is one of the most highly-industrialised and economically powerful countries in the world. The economic system is classed as a social market economy within which competition has become very pronounced. Unemployment is a problem, not only in the new Federal States. The major sectors of the economy are manufacturing industry, service industries and trade, and transport. Great political importance is attached to environmental protection which is a major concern of the people. Germany is one of the most highly-industrialised and economically powerful countries in the world. The economic system is classed as a social market economy within which competition has become very pronounced. Unemployment is a problem, not only in the new Federal States. The major sectors of the economy are manufacturing industry, service industries and trade, and transport. Great political importance is attached to environmental protection which is a major concern of the people.
 |
Web Links |
 |
| Background information about Germany |
 |
Germany Tourism |
The website of the German National Tourist Office in London takes you on a fascinating journey through Germany and aims to inspire you to visit. |
 |
CIA World Factbook |
The CIA World Factbook provides a factual overview of the current state of Germany. |
 |
Facts about Germany |
An English-language introduction to the German nation from the German embassy in Wahington D.C. |
 |
Statistics about Germany |
This web-site offers statistical information about the Federal Republic of Germany on a broad range of themes including population, employment, accommodation, education, culture, economics, the legal system and the environment. |
 |
Meine Stadt im Internet |
This site offers information portals on over 14,000 towns and cities in Germany, listing local media, tourist information and statistical data. |
|
 Chapter 2.11: German history Chapter 2.11: German history

 Print This Page Print This Page
|