5.6 The dative case and the articles
Definite article
The endings for the definite article "der" in the dative case are as follows - singular endings only.
| Grammar 3: Definite article in the dative case |
| |
Masculine |
Feminine |
Neuter |
| Nominative |
der Mann |
die Frau |
das Kind |
| Accusative |
den Mann |
die Frau |
das Kind |
| Dative |
dem Mann |
der Frau |
dem Kind |
|
Merging of prepositions with the definite article
You will already have noted that certain prepositions tend to merge with the definite article - but never with the indefinite article. The following contracted forms are almost always preferred to the non-contracted forms:
| Grammar 4: Dative prepositions |
| |
Prep. |
Example |
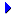 |
an + dem = am |
Ich bin am U-Bahnhof
(I am at the underground station) |
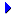 |
in + dem = im |
Wir sind im Café
(We are in the café) |
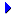 |
von + dem = vom |
Zehn Minuten vom Bahnhof
(Ten minutes from the station) |
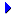 |
zu + dem = zum |
Wie komme ich zum Hotel?
(How do I get to the hotel?) |
 |
zu + der = zur |
Sie geht zur Bank
(She goes to the bank) |
|
The indefinite article
The endings for the indefinite article "ein" in the three cases which we have met so far are printed below. Note that "kein" also declines in the same way.
| Grammar 5: Indefinite article in the dative case |
| |
Masculine |
Feminine |
Neuter |
| Nom. |
ein Mann |
eine Frau |
ein Kind |
| Acc. |
einen Mann |
eine Frau |
ein Kind |
| Dat. |
einem Mann |
einer Frau |
einem Kind |
|
Possessive adjectives
The endings for the possessive adjectives are as follows. We have given "mein" as an example, but the others decline in the same way.
| Grammar 6: Possessive adjectives in the dative case |
| |
Masc. |
Fem. |
Neut. |
| Nom. |
mein Mann |
meine Frau |
mein Kind |
| Acc. |
meinen Mann |
meine Frau |
mein Kind |
| Dat. |
meinem Mann |
meiner Frau |
meinem Kind |
|
The only exception to this rule is the possessive adjective "euer" (= your). This possessive loses the "-e-" of its stem when it adds endings.
| Grammar 7: The possessive "euer" in the dative case |
| |
Masc. |
Fem. |
Neut. |
| Nom. |
euer Mann |
eure Frau |
euer Kind |
| Acc. |
euren Mann |
eure Frau |
eurer Kind |
| Dat. |
eurem Mann |
eurer Frau |
eurem Kind |
|
 Chapter 5.7: Adjectives Chapter 5.7: Adjectives

 Print This Page Print This Page
|